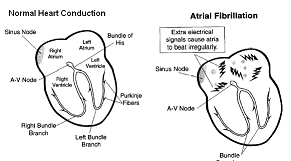
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is an abnormal irregular heart rhythm. Normally, your heart contracts and relaxes to a regular beat. The sinus node is your heart’s natural pacemaker. It sends electrical signals to the rest of your heart through the conduction system, which
consists of the AV node, Bundle of His, bundle branches and Purkinje fibers. These signals cause your heart to contract and pump blood. In atrial fibrillation, the sinus node does not start the electrical signal, but rather signals come from the atria. This
causes the heart to beat irregularly, and at times too fast.
Signs and Symptoms:
* Irregular heart beat
* Heart palpitations or the feeling of rapid thumping inside the chest
* Shortness of breath
* Tire easily with activity
* Lightheadedness, dizziness, or you may even feel faint
Treatments:
* Medicine
You may have to take medicine such as Digoxin (Lanoxin) or a calcium channel blocker, such as Cardizem, to help regulate your heart rhythm and rate. You may also have to take anticoagulant medication such as Coumadin, to reduce the risk of
blood clots and stroke.
* Cardioversion
If medicine is not successful in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, you may have to have a procedure called cardioversion. Cardioversion is a low energy electrical shock applied through the skin to the heart. Cardioversion converts an abnormal
heart rhythm to a normal rhythm.
Difference Between Acute and Chronic Atrial Fibrillation:
Acute atrial fibrillation is the sudden onset of the heart beating irregularly and usually with a fast rate. You will usually have symptoms if your condition is acute. In chronic atrial fibrillation, the heart beats irregularly all the time. Acute atrial fibrillation is usually treated first with Cardioversion to return the heart to a normal rhythm. Then medicines are used to keep the heart beat regular. In chronic atrial fibrillation, medicines only are used to convert the rhythm to normal and/or keep
the heart from beating too fast. It is very important that you be under a doctor’s care to monitor the atrial fibrillation.
You can live with chronic atrial fibrillation, but it can cause stroke or serious heart rhythm disturbances if not controlled!
Treating atrial fibrillation is an important way to help prevent stroke. That's why the American Heart Association recommends aggressive treatment of this heart arrhythmia, following these guidelines:
· Atrial fibrillation should be treated with some form of preventive medication prescribed and monitored by a physician.
· Aspirin and warfarin, the currently used medications, can have a major beneficial effect on public health in the United States.
· Physicians differ on the choice of drugs to prevent embolic stroke — stroke caused by an embolus (blood clot). It's clear that warfarin is more effective against this type of stroke than aspirin. However, warfarin has side effects, such as abnormal bleeding, especially in older patients.
· Warfarin in well-regulated doses that lead to a moderate interference with clotting is effective and appears safe in many patients.